0基础学微信小程序开发(一)基本介绍
本文共 679 字,大约阅读时间需要 2 分钟。
目录
小程序介绍
小程序开发作为腾讯17年推出的一块开发工具,目前已经培养了大量的开发人员,今年的峰会上已经有超过100万开发者选择了小程序,尤其是初创团队特别适合。作为微信推出的工具,感觉有几个特点,一是技术体系完善,二是社区丰富,三是文档友好。新手其实也是蛮适合入手的,现在是移动互联网的时代,能快速的掌握移动端开发的技能也是蛮好的。
账号注册
注册了账号之后,先需要下载开发工具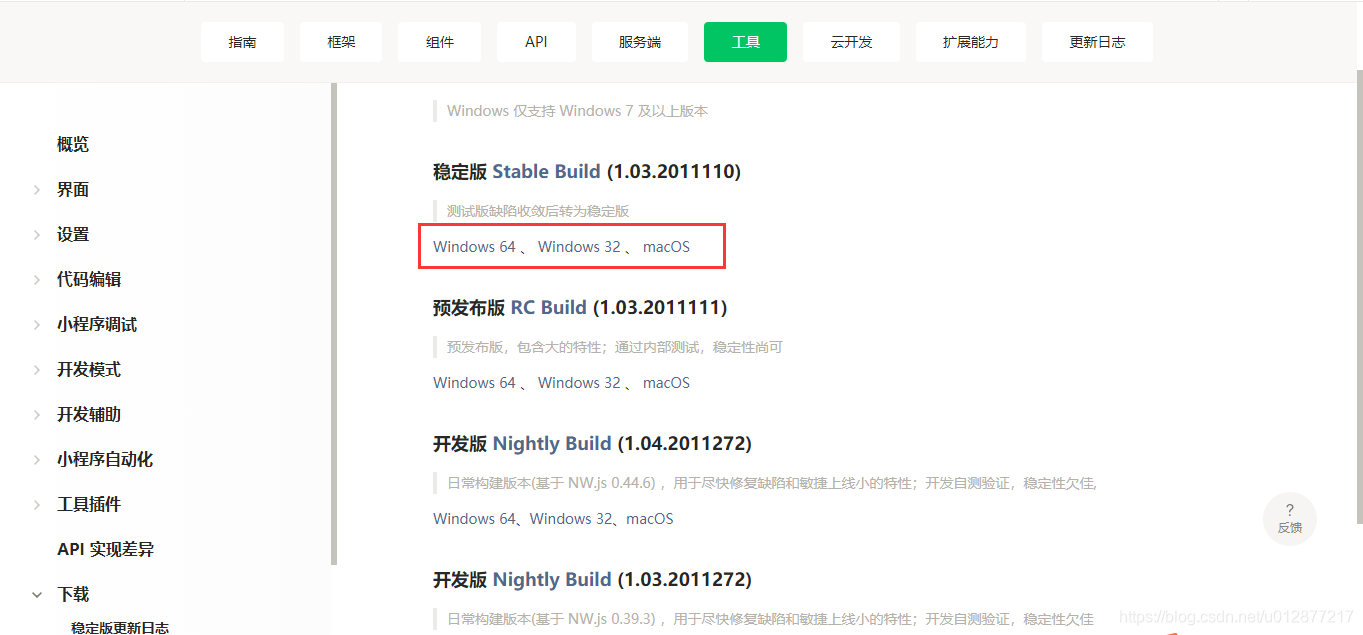 根据需要选择版本下载安装 工具启动后,新建项目
根据需要选择版本下载安装 工具启动后,新建项目 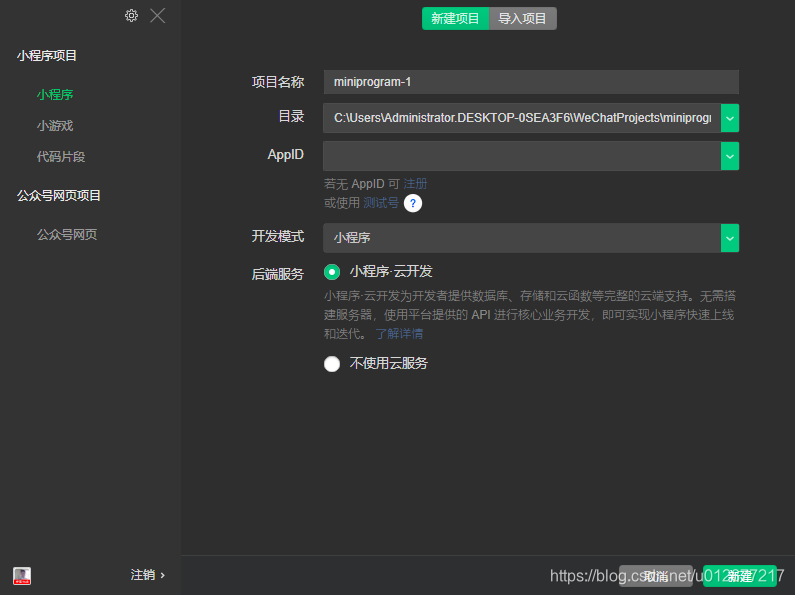 目录需要新建一个空目录,项目名称可以自己定义,APPID是自己申请账号时就已经确定了
目录需要新建一个空目录,项目名称可以自己定义,APPID是自己申请账号时就已经确定了 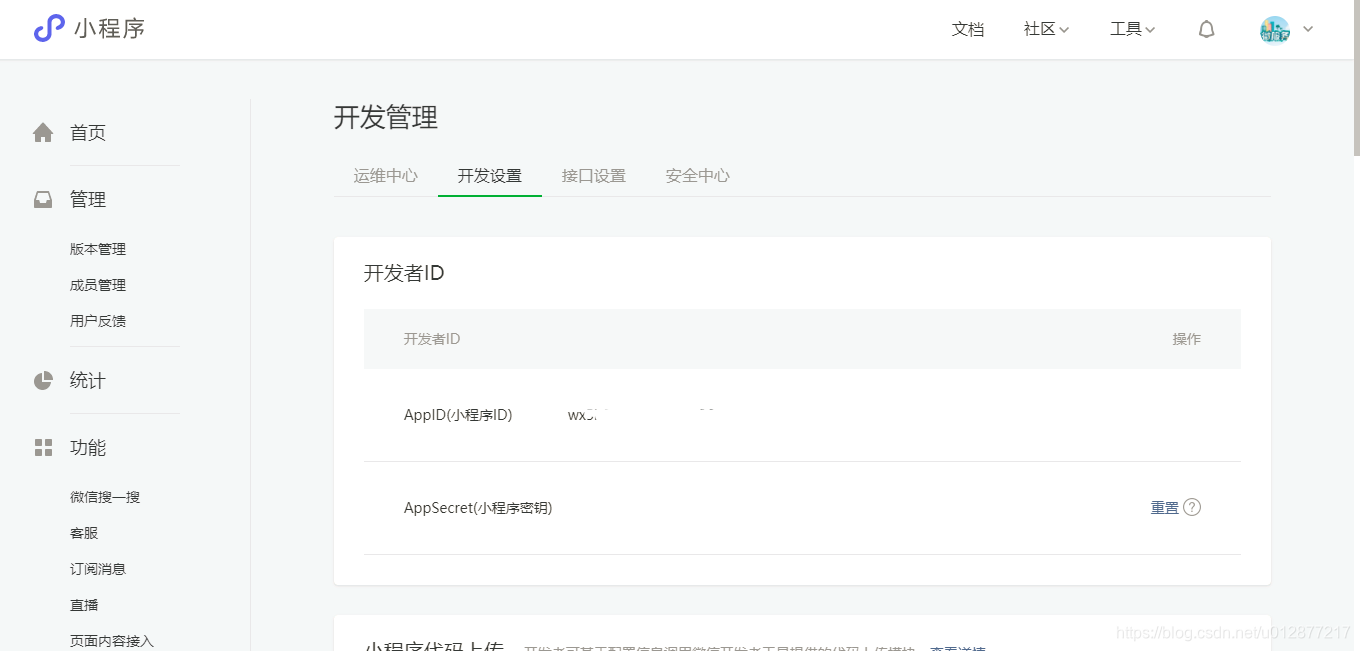 后端开发我们选择小程序-云开发,云环境为我们提供了数据库,后台服务,调用也比较方便
后端开发我们选择小程序-云开发,云环境为我们提供了数据库,后台服务,调用也比较方便 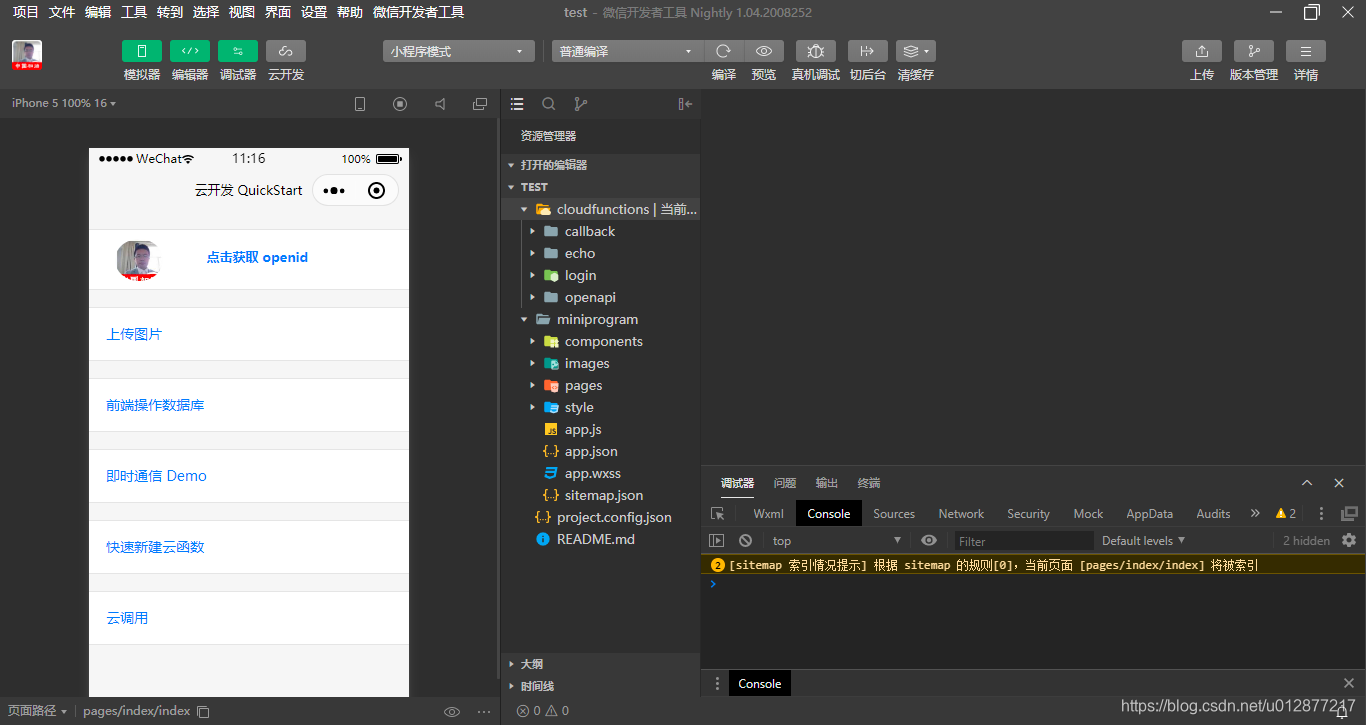 功能介绍,左边是程序的预览区,可以直观看到你写的代码的表现形式;中间一栏是代码的结构,右边是代码的编辑区域
功能介绍,左边是程序的预览区,可以直观看到你写的代码的表现形式;中间一栏是代码的结构,右边是代码的编辑区域 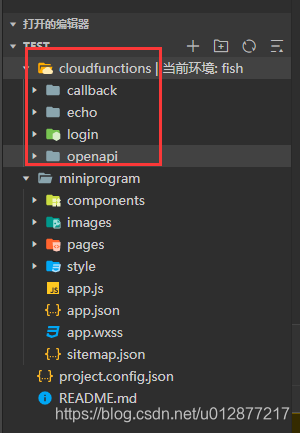 cloudfunctions是云函数的区域,基本上我们一个后台方法就需要一个云函数支持
cloudfunctions是云函数的区域,基本上我们一个后台方法就需要一个云函数支持 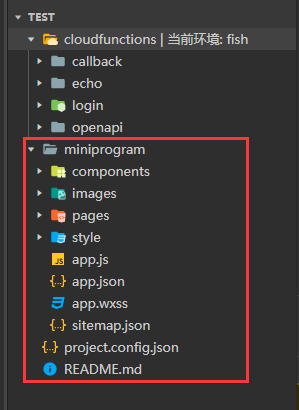 miniprogram相当于前端的区域,页面的样式、组件、交互逻辑都需要在这里写
miniprogram相当于前端的区域,页面的样式、组件、交互逻辑都需要在这里写 官方文档
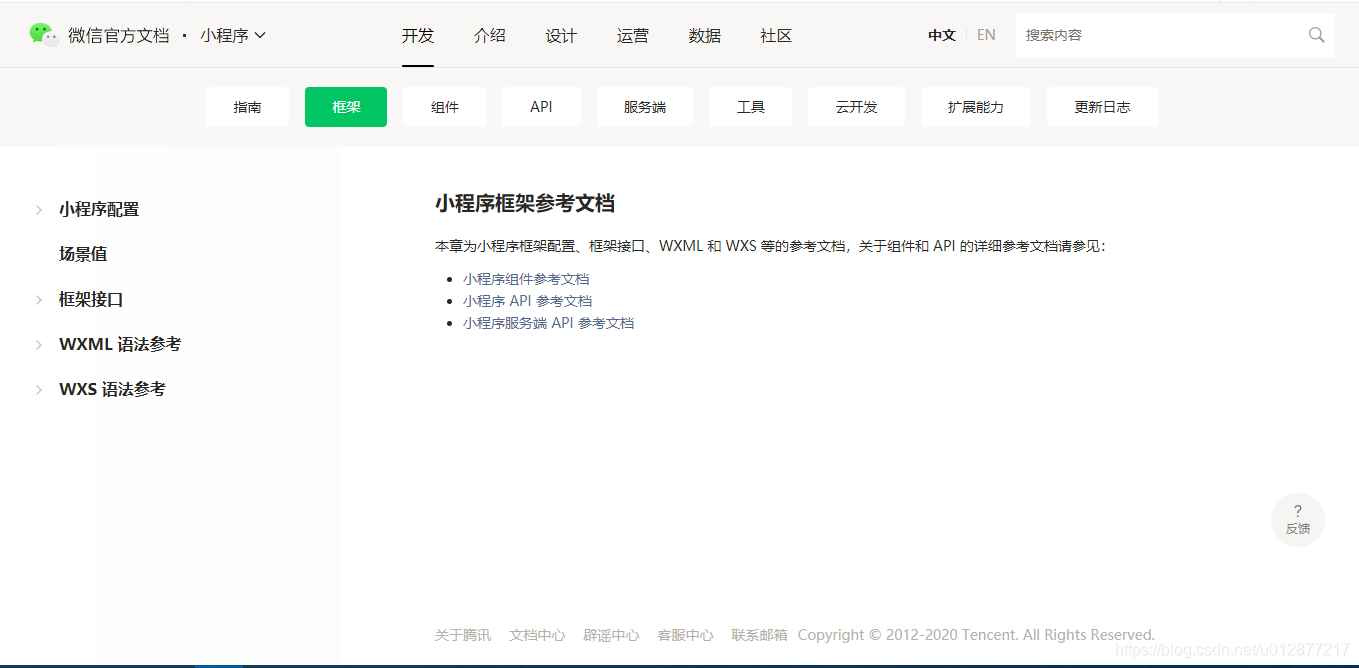 指南是对总体功能的一个介绍,包括开发流程的 框架,需要搞明白小程序是怎么交互的,比如wxss是写样式的,wxml是组件的编写地方,js是定义逻辑的地方 组件,可以调用的各类组件,比如容器组件view,文本组件text API,微信开发的各类工具类 服务端,这个就是更高级一点的功能,用到的时候查看一下 云开发,这个是讲述后台的各类操作,比如访问数据库,访问存储
指南是对总体功能的一个介绍,包括开发流程的 框架,需要搞明白小程序是怎么交互的,比如wxss是写样式的,wxml是组件的编写地方,js是定义逻辑的地方 组件,可以调用的各类组件,比如容器组件view,文本组件text API,微信开发的各类工具类 服务端,这个就是更高级一点的功能,用到的时候查看一下 云开发,这个是讲述后台的各类操作,比如访问数据库,访问存储 总结
这一篇我们分析了小程序的基本功能,和官方文档的大致介绍,下一篇我们开始一点点的学习小程序的具体使用
转载地址:http://djbzz.baihongyu.com/
你可能感兴趣的文章
MySQL不会性能调优?看看这份清华架构师编写的MySQL性能优化手册吧
查看>>
MySQL不同字符集及排序规则详解:业务场景下的最佳选
查看>>
Mysql不同官方版本对比
查看>>
MySQL与Informix数据库中的同义表创建:深入解析与比较
查看>>
mysql与mem_细说 MySQL 之 MEM_ROOT
查看>>
MySQL与Oracle的数据迁移注意事项,另附转换工具链接
查看>>
mysql丢失更新问题
查看>>
MySQL两千万数据优化&迁移
查看>>
MySql中 delimiter 详解
查看>>
MYSQL中 find_in_set() 函数用法详解
查看>>